Managing Risk at Commercial Bank
Comparison of Exposures with Risk Policy Parameters
| Risk Category and Parameter |
Description | Policy Range | Actual Position as at 31.12.2011 |
Compliance | |||||||||||
| Credit Risk Criteria | |||||||||||||||
| Quality of the Lending Portfolio |
Gross NPA Ratio** | 4% - 5% | 3.43% | ||||||||||||
| Net NPA Ratio** | 2.5% - 3.5% | 2.08% | |||||||||||||
| Provision Cover | 35% - 40% | 39.53% | |||||||||||||
| Aggregate Loans & Advances in the Risk Grades ‘C - A5’ | 75% - 80% | 87.03% | |||||||||||||
| Weighted Average Rating of the overall lending portfolio to be better than ‘A5’ | 40% - 45% | 45.62% | |||||||||||||
| Concentration | Loans & Advances by Product*** (using HHI) | 0.15 - 0.20 | 0.1746 | ||||||||||||
| Advances by Economic sub-sector (using SIC)*** (using HHI) | 0.015 - 0.025 | 0.0159 | |||||||||||||
| Exposures exceeding 5% of the Eligible Capital*** (using HHI) | 0.05 - 0.10 | 0.05247 | |||||||||||||
| Exposures exceeding 15% of the Eligible Capital*** (using HHI) | 0.10 - 0.20 | 0.1322 | |||||||||||||
| Exposure to any sub-sector (SIC) to be maintained | 4% - 5% | 4.8% | |||||||||||||
| Aggregate of Exposures exceeding 15% of the Eligible Capital | 20% - 30% | 19.11% | |||||||||||||
| Lending in the Maldives | Maximum 20% of Net Worth | 11.97% | |||||||||||||
| Lending to Bangladesh Branch | Maximum USD 15 Mn. | USD 4.84 Mn. | |||||||||||||
| Cross boarder exposure | S & P: - AAA to BBB - | Over 75% | 90.72% | ||||||||||||
| Exposure to the Government |
FCY Investment | Maximum USD 250 Mn. | USD 201.0 Mn. | ||||||||||||
| FCY Trading (S/L) | Maximum USD 50 Mn. | USD 49.0 Mn. | |||||||||||||
| Cumulative stop loss for FCY trading portfolio | Maximum USD 3.75 Mn. | No loss | |||||||||||||
| Market Risk Criteria | |||||||||||||||
| Interest Rate Risk | Interest Rate Shock (Impact to NII as a result of parallel rate shock) | Maximum of 800 (Rs. Mn.) | Rs. 882.09 Mn. | ||||||||||||
| Re-pricing Gaps (RSA/RSL in each maturity bucket) | 1.5 (Times) | 0.06-6.04 | |||||||||||||
| Liquidity Risk | Statutory Liquid Assets Ratio (CBSL Guidelines) - DBU | Minimum of 20% | 25.70% | ||||||||||||
| Net Advances to Deposits Ratio | Below 90% | 86.06% | |||||||||||||
|
0.5 (Times) | -0.54 | |||||||||||||
| 0.5 (Times) | -0.09 | ||||||||||||||
| Less than 1 (Times) | 0.11 | ||||||||||||||
|
50% | 7.96 | |||||||||||||
| 15% | (+) PG | ||||||||||||||
| 20% | (+) PG | ||||||||||||||
| 20% | (+) PG | ||||||||||||||
| FX Risk | Exchange Rate Shocks (Losses as a result of 1% change in FX Rate) | Maximum of 250 (Rs. Mn) | Rs. 88.09 Mn. | ||||||||||||
| Concentration Risk | - Rupee Deposit Concentration | ||||||||||||||
| - Savings & Demand Deposits above LKR 5.0 Mn. | Below 5% | <4.00% | |||||||||||||
| - Fixed deposits above Rs. 10.0 Mn. | Below 5% | <4.00% | |||||||||||||
| - FCY Deposit Concentration (Above USD 100,000 or equivalent) | Below 60% | 55.85% | |||||||||||||
| Operational Risk Criteria | |||||||||||||||
| Internal Fraud | Acts of a type intended to defraud, misappropriate property or circumvent regulations, etc. |
0.30% - 0.50%# | 0.0034% | ||||||||||||
| External Fraud | Acts of a type intended to defraud, misappropriate property or circumvent the law, by a third party |
1.5% - 2.5%# | 0.0745% | ||||||||||||
| Employment Practices and Workplace Safety | Acts inconsistent with employment, health or safety laws or agreements, from payment of personal injury claims, or from diversity/discrimination events |
0.06% - 0.1%# | – | ||||||||||||
| Clients, Products & Business Practices |
Unintentional or negligent failure to meet a professional obligation to specific clients, etc. |
0.09% - 0.15%# | – | ||||||||||||
| Damage to Physical Assets |
Loss or damage to physical assets from natural disasters or other events | 0.30% - 0.50%# | 0.0061% | ||||||||||||
| Business Disruption & System Failures |
Disruption of business or system failures | 0.15% - 0.25%# | 0.0823% | ||||||||||||
| Execution, Delivery & Process Management |
Failed transactions processing or process management | 0.60% - 1.00%# | 0.1151% | ||||||||||||
| Overall - Operational Risk |
Operational Loss Tolerance Limit (Total Loss Value as a percentage of last three years‘ average gross income) |
3% - 5% | 0.2813% | ||||||||||||
| ** For the Total Bank *** (Using Herfindahl - Hirschman Index - HHI) RSA - Rate Sensitive Assets; RSL - Rate Sensitive Liabilities; PG - Period Gap; CO - Cash Outflows # Value as a percentage of maximum Operational Loss Tolerance Limit |
|||||||||||||||
Capital Adequacy
Capital adequacy is a measure of the financial strength of a bank expressed as a ratio of its capital to its risk weighted assets. This ratio indicates a bank’s ability to maintain adequate equity capital to repay its depositors on demand and still have enough funds to increase the bank’s assets through additional lending. At Commercial Bank too, we compute the Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) in accordance with the Basel II accord.Basel Accord
The Basel capital accord is an agreement between countries’ central banks and bank supervisory authorities on the amount of capital banks must hold as a cushion against losses and insolvency. Higher capital requirements constrain bank lending and profitability.In 1999, the Basel Committee decided to propose a new, more comprehensive capital adequacy accord in response to the banking crises of the 1990s and the criticisms of Basel I. This accord is known formally as 'A Revised Framework on International Convergence of Capital Measurement and Capital Standards’ and informally as ‘Basel II’ greatly expands the scope, technicality, and depth of the original Basel Accord. While maintaining the ‘pillar’ framework of Basel I, each pillar is greatly expanded in Basel II to cover new approaches to credit risk, adapt to the securitization of bank assets, cover market, operational, and interest rate risk, and incorporate market based surveillance and regulation.
Basel II Framework
The key components of the Basel II framework and the corresponding approaches are demonstrated in the Table below. Further, the approaches adopted by the Bank are also indicated in the same.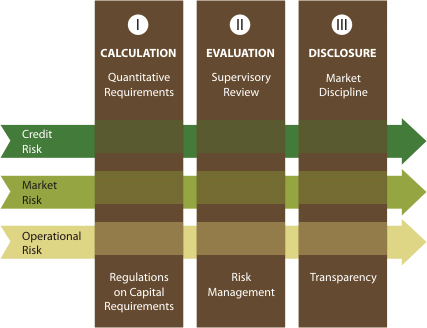
Pillar Framework of Basel II |
|||
| Pillar I | Minimum Capital Requirement | ||
| This represents the calculation of the total minimum capital requirements for credit, market and operational risk. The capital ratio is calculated using the definition of regulatory capital and risk-weighted assets. The total capital ratio must be no lower than 10%. | |||
| Credit Risk | Standardized Approach | ||
| Foundation Internal Ratings Based Approach (FIRB) | |||
| Advanced Internal Ratings Based Approach (AIRB) | |||
| Market Risk | Standardised Measurement Approach | ||
| Advanced Measurement Approach | |||
| Operational Risk | Basic Indicator Approach | ||
| Standardised Approach | |||
| Advanced Measurement Approach | |||
| Pillar II | Supervisory Review Process | ||
| The supervisory review process of the framework is intended not only to ensure that banks have adequate capital to support all the risks in their business, but also to encourage banks to develop and use better risk management techniques in monitoring and managing their risks. It also recognises the responsibility of bank management in developing an Internal Capital Adequacy Assessment Process (ICAAP) and setting capital targets that are commensurate with the bank’s risk profile and control environment. | |||
| Pillar III | Market Discipline | ||
| This is to complement the requirements under Pillar I and Pillar II. It aims to encourage market discipline by developing a set of disclosure requirements which will allow market participants to assess key pieces of information on the scope of application, capital, risk exposures, risk assessment processes. | |||
| On-Balance Sheet - Assets and Credit Equivalent of Off-Balance Sheet Assets |
Risk -Weighted Balance | ||||
| 2011 Rs. ‘000 |
2010 Rs. ‘000 |
Risk-Weight Factor (%) |
2011 Rs. ‘000 |
2010 Rs. ‘000 |
|
Assets |
|||||
| Claims on Government of Sri Lanka and Central Bank of Sri Lanka | 100,500,592 | 108,059,692 | 0 | – | – |
| Claims on Foreign sovereigns and their Central Banks | 7,589,925 | 7,288,779 | 0-150 | 7,589,925 | 7,288,779 |
| Claims on Public Sector Entities (PSEs) | 19,395 | 27,660 | 20-150 | 19,395 | 27,660 |
| Claims on Official Entities and Multilateral Development Banks (MDBs) | – | – | 20-150 | – | – |
| Claims on Banks | 18,417,892 | 5,836,513 | 0-150 | 6,833,718 | 3,178,266 |
| Claims on Financial Institutions | 2,644,000 | 1,126,800 | 20-150 | 1,729,350 | 777,750 |
| Claims on Corporates | 168,245,189 | 181,686,544 | 20-150 | 157,204,758 | 173,266,572 |
| Retail Claims | 69,487,773 | 18,413,845 | 75-100 | 57,519,874 | 18,413,845 |
| Claims Secured by Residential Property | 24,105,257 | 19,106,565 | 50-100 | 24,105,257 | 15,229,147 |
| Claims Secured by Commercial Real Estate | – | – | 100 | – | – |
| Non-Performing Assets (NPAs) | 6,197,613 | 6,191,125 | 50-150 | 8,389,062 | 8,334,882 |
| Cash Items | 8,576,710 | 6,192,757 | 0 | 7,572 | 1,758 |
| Property, Plant & Equipment | 8,616,445 | 6,703,918 | 100 | 8,616,445 | 6,703,918 |
| Other Assets | 8,059,096 | 6,183,157 | 100 | 8,059,096 | 6,183,157 |
| Total | 422,459,886 | 366,817,356 | 280,074,452 | 239,405,735 | |
| Credit Conversion | |||||
| Credit Equivalent | |||||
| 2011 Rs. ’000 |
2010 Rs. ’000 |
Factor % | 2011 Rs. ’000 |
2010 Rs. ’000 |
|
| Instruments | |||||
| Direct Credit Substitutes | 17,784,925 | 21,117,004 | 100 | 17,784,925 | 21,117,004 |
| Transaction-Related Contingencies | 7,703,979 | 6,207,068 | 50 | 3,851,990 | 3,103,534 |
| Short Term Self-Liquidating Trade-Related Contingencies | 39,736,030 | 33,960,523 | 20 | 7,947,206 | 6,792,105 |
| Sale and Repurchase Agreements and Assets Sale with recourse where the credit risk remains with the Bank |
– | – | 100 | – | – |
| Obligations under an on going Underwriting Agreement | – | – | 50 | – | – |
| Other Commitments with an original maturity of up to one year or which can be unconditionally cancelled at any time |
59,691,611 | 49,001,044 | 0 | – | – |
| Commitments with an original maturity up to 1 year | – | – | 20 | – | – |
| Other Commitments with an original maturity of over one year | – | – | 50 | – | – |
| Foreign Exchange Contracts | 104,398,912 | 80,486,733 | 0-5 | 2,087,978 | 1,609,735 |
| Interest Rate Contracts | 50,806 | 576,868 | 0-3 | 1,524 | 13,520 |
| Total | 229,366,263 | 191,349,240 | 31,673,623 | 32,635,898 | |
| 2011 | 2010 | |
| Item | Rs. ’000 | Rs. ’000 |
Capital Charge for Market Risk |
||
| Capital Charge for Interest Rate Risk | 254,149 | 252,058 |
| Capital Charge for Equity | 41,119 | 32,639 |
| Capital Charge for Foreign Exchange and Gold | 68,269 | 57,004 |
| Total Capital Charge for Market Risk | 363,537 | 341,701 |
| Total Risk Weighted Assets for Market Risk | 3,635,371 | 3,417,009 |
Capital Charge for Operational Risk |
||
| Gross Income | ||
| Year 1 | 19,236,720 | 16,226,822 |
| Year 2 | 20,121,710 | 19,236,720 |
| Year 3 | 23,166,112 | 20,121,710 |
| Average Gross Income | 20,841,514 | 18,528,417 |
| Total Capital Charge for Operational Risk - (15%) | 3,126,227 | 2,779,263 |
| Total Risk-Weighted Assets for Operational Risk | 31,262,271 | 27,792,626 |
Computation of Capital |
||
| Tier I: Core Capital | ||
| Paid-up Ordinary Shares | 17,945,271 | 11,566,166 |
| Statutory Reserve Fund | 2,740,902 | 2,338,511 |
| Published Retained Profits/(Accumulated Losses)(+/-) | 43,865 | 28,056 |
| General and Other Reserves | 17,856,434 | 15,866,038 |
| Minority Interests (consistent with the above capital constituents) | 29,615 | 24,980 |
| Less: | ||
| Other Intangible Assets | (475,038) | (425,255) |
| Advances granted to employees of the Bank for the purchase of shares of the Bank (ESOP) | (2,105) | (3,068) |
| 50% Investments in the Capital of Other Banks and Financial Institutions | (402) | (5,402) |
| Total Eligible Core Capital (Tier I Capital) | 38,138,542 | 29,390,025 |
| Tier II : Supplementary Capital | ||
| Revaluation Reserves (as approved by Central Bank of Sri Lanka) | 651,037 | 651,037 |
| General Provisions | 1,201,991 | 1,709,481 |
| Approved Subordinated Term Debt | 972,880 | 1,426,154 |
| Less: | ||
| 50% Investments in the Capital of Other Banks and Financial Institutions | (402) | (5,402) |
| Total Eligible Supplementary Capital (Tier II Capital) | 2,825,506 | 3,781,270 |
| Total Capital Base | 40,964,048 | 33,171,295 |
Computation of Ratios |
||
| 2011 | 2010 | |
| Rs. ’000 | Rs. ’000 | |
| Total Risk-Weighted Assets (RWA) | ||
| Total Risk-Weighted Assets for Credit Risk | 280,074,154 | 239,405,735 |
| Total Risk-Weighted Assets Market Risk | 3,635,371 | 3,417,009 |
| Total Risk-Weighted Assets Operational Risk | 31,262,271 | 27,792,626 |
| Sub Total | 314,971,795 | 270,615,370 |
| Minimum Capital Charge | ||
| Minimum Capital Charge for Credit Risk | 28,007,415 | 23,940,573 |
| Minimum Capital Charge for Market Risk | 363,537 | 341,701 |
| Minimum Capital Charge for Operational Risk | 3,126,227 | 2,779,263 |
| Sub Total | 31,497,180 | 27,061,537 |
| Total Capital available to meet the Capital Charge for Credit Risk | ||
| Total Eligible Core Capital (Tier I Capital) | 38,138,542 | 29,390,025 |
| Total Eligible Supplementary Capital (Tier II Capital) | 2,825,506 | 3,781,270 |
| Total Capital Base | 40,964,048 | 33,171,295 |
Core Capital Ratio (Minimum Requirement 5%) |
||
| Total Eligible Core Capital (Tier I Capital ) | 38,138,542 | 29,390,025 |
| Total Risk-Weighted Assets | 314,971,795 | 270,615,370 |
| 12.11% | 10.86% | |
Total Capital Ratio (Minimum Requirement 10%) |
||
| Total Capital Base | 40,964,048 | 33,171,295 |
| Total Risk-Weighted Assets | 314,971,795 | 270,615,370 |
| 13.01% | 12.26% |


