Managing Risk at Commercial Bank
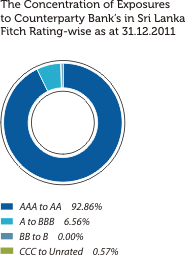
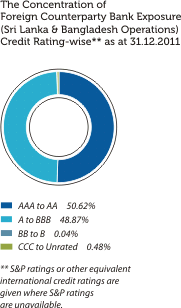
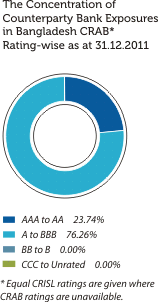
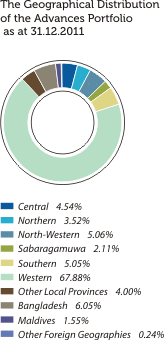
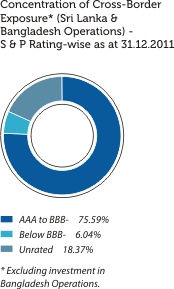
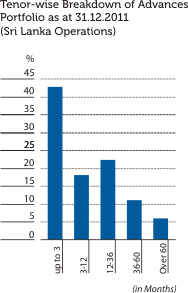
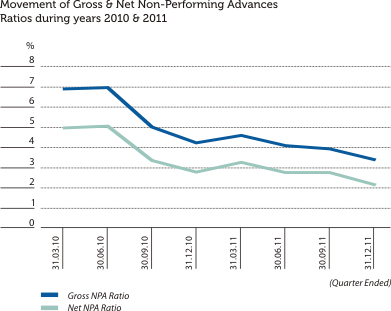
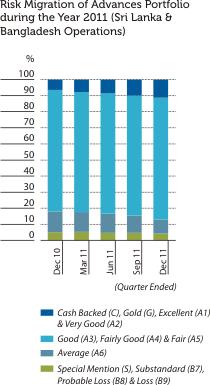
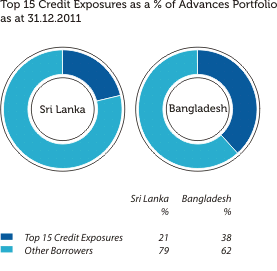
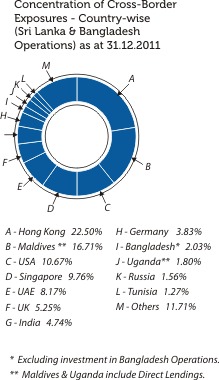
The graphical presentations below depict the analysis of the Bank’s overall credit risk exposure as at December 31, 2011 based on different factors. Industry Sector distribution of the Advances Portfolio is given under Sustainability Supplement.
Distribution of Specific Provision as at December 31, 2011
| Exposure
(Net of Suspense and Security) |
Minimum Provision Requirement as per CBSL Direction |
Specific Provision Already Held |
|||
| Rs. ’000 | Rs. ’000 | % | Rs. ’000 | % | |
| Special Mention | 1,263,868 | – | – | – | – |
| Substandard | 316,014 | 63,203 | 20 | 277,341 | 87.76 |
| Doubtful | 123,224 | 61,612 | 50 | 205,231 | 166.55 |
| Loss | 2,723,586 | 2,723,586 | 100 | 3,238,628 | 118.91 |
| Total | 4,426,692 | 2,848,401 | 3,721,200 | ||
Credit Risk Mitigation and Control
The Bank believes that credit risk management should be a value enhancing activity that goes beyond regulatory compliance encompassing:- An appropriate credit risk environment which seeks risk optimisation;
- A sound credit approval and granting process;
- An appropriate credit administration, measurement and monitoring process; and
- Adequate controls over credit risk on a continuous basis.
extent. The Bank’s credit portfolio is also subjected to continuous review at various levels which provide an early warning on any impending deterioration of the Bank’s credit quality. The overall credit risk exposure on certain risk categories (i.e. single borrower, industrial/service sectors, special products etc.) are monitored and controlled through establishment of prudential limits, within the risk appetite framework of the Bank.
At individual exposure level, most common traditional credit risk mitigant is the collaterals provided by the borrowers. These include Mortgage over properties, Lien over deposits, Guarantees etc. The Bank as a policy obtain professional valuations when fixed assets are taken as collateral and these values are periodically monitored by the Lending Officers.
The primary objective of the Market Risk Management Unit (MRMU) of Integrated Risk Management Department (IRMD) is to ensure that the rewards are optimised in Bank’s business transactions which are exposed to various market risks while maintaining the down side risks under control within approved policy limits/parameters and guidelines. In order to achieve this, MRMU constantly maintains a close working relationship with the risk assuming business lines and control/monitoring functions within the Bank.
At individual exposure level, most common traditional credit risk mitigant is the collaterals provided by the borrowers. These include Mortgage over properties, Lien over deposits, Guarantees etc. The Bank as a policy obtain professional valuations when fixed assets are taken as collateral and these values are periodically monitored by the Lending Officers.
MARKET RISK
The Bank encounters, risk of losses in 'On Balance-Sheet’ and ‘Off-Balance Sheet’ positions arising from movements in market prices and this is defined as Market Risk as per Basel II. Banks are exposed to Market Risk not only due to trading activities, but also due to engaging in non-trading activities such as Lending, Corporate Investments and Equity Investments.The primary objective of the Market Risk Management Unit (MRMU) of Integrated Risk Management Department (IRMD) is to ensure that the rewards are optimised in Bank’s business transactions which are exposed to various market risks while maintaining the down side risks under control within approved policy limits/parameters and guidelines. In order to achieve this, MRMU constantly maintains a close working relationship with the risk assuming business lines and control/monitoring functions within the Bank.


