Managing Risk at Commercial Bank
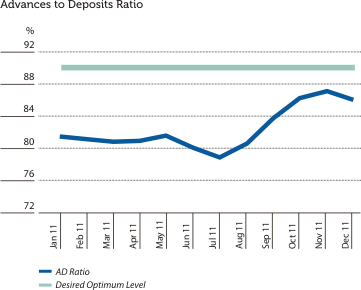
ALCO regularly monitors the Net Advances to Deposit Ratio of the Bank to ensure that the Bank maintains a healthy liquidity position in its main asset and liability portfolios. The Bank managed to maintain the Advances to Deposits Ratio at a satisfactory level as depicted in the graph below.
Banking industry in Sri Lanka experienced a dwindling liquidity position during the latter part of the year 2011, from an excess of about Rs. 121.18 Bn. as at the beginning of the year to a short fall of Rs. 5.38 Bn. recorded at year end as depicted in the graph below.
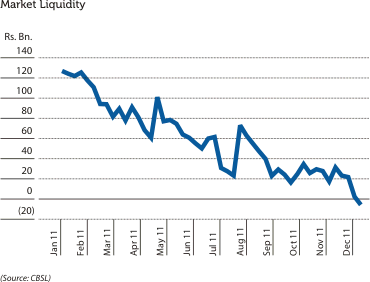
ALCO monitors the market liquidity which provides an insight into the ability of the Bank to fulfil its funding requirements from market sources at a reasonable price and decides on an alternative course of action if required.
Further, Bank also conducts regular liquidity stress tests based on certain assumed scenarios, which provides vital information to formulate contingency funding plans. Further, the Bank has also signed a reciprocal Contingency Funding Plan with a suitable counterparty to overcome any unforeseen tight liquidity situations.
Bank has a Board approved Liquidity Funding Plan in place, which details out the contingency plans to overcome any funding crisis. Further, Bank monitors trends in Net Loans to Total Assets Ratio to ensure that the ratio remains within the internally approved threshold. Maturities of assets and liabilities too are monitored to identify any gaps that need to be addressed.
Further, Bank also conducts regular liquidity stress tests based on certain assumed scenarios, which provides vital information to formulate contingency funding plans. Further, the Bank has also signed a reciprocal Contingency Funding Plan with a suitable counterparty to overcome any unforeseen tight liquidity situations.
Liquidity Risk Monitoring, Mitigation and Control
Regulatory framework of the Bank on liquidity has been formulated in compliance with CBSL guidelines and they include Statutory Reserve Ratio, which is managed by Bank’s Treasury on a weekly basis ensuring that 8% of the average daily LKR deposits are maintained at CBSL and Statutory Liquid Asset Ratio maintained with a margin of safety above the stipulated regulatory level of 20.0%.Bank has a Board approved Liquidity Funding Plan in place, which details out the contingency plans to overcome any funding crisis. Further, Bank monitors trends in Net Loans to Total Assets Ratio to ensure that the ratio remains within the internally approved threshold. Maturities of assets and liabilities too are monitored to identify any gaps that need to be addressed.
OPERATIONAL RISK
Operational Risk can be defined as the risk of loss resulting from inadequate or failed internal processes, people and systems or from external events. The definition includes the legal risk, which is the risk of loss resulting from failure to comply with laws and regulatory requirements.
Key Processes of the Management of Operational Risk in the Bank are based on the concept of ‘Risk vs Service vs Cost’. Operational Risk is managed with least inconvenience to the clients in a cost effective manner so that the risk exposures of the Bank’s business operations are optimised to enhance business opportunities.
Comprehensive training and development programmes are conducted on an ongoing basis to enhance awareness on Operational Risk mechanisms among risk owners of the Bank. This continuous skill development programme facilitates to inculcate a robust risk culture in the Bank which will have long term benefits.
Further, a comprehensive Operational Risk Management Policy which addresses the governance structure for Operational Risk Management is in place to support the overall Operational Risk Strategy of the Bank.
Operational Risk Management responsibilities at the Corporate Management level are carried out by the Executive Integrated Risk Management Committee (EIRMC) which is represented by all senior Risk Owners and Risk Managers. EIRMC is responsible for monitoring regular Operational Risk Indicators in accordance with the established policies and procedures and taking corrective actions where deemed necessary.
Comprehensive training and development programmes are conducted on an ongoing basis to enhance awareness on Operational Risk mechanisms among risk owners of the Bank. This continuous skill development programme facilitates to inculcate a robust risk culture in the Bank which will have long term benefits.
Further, a comprehensive Operational Risk Management Policy which addresses the governance structure for Operational Risk Management is in place to support the overall Operational Risk Strategy of the Bank.
Operational Risk Management responsibilities at the Corporate Management level are carried out by the Executive Integrated Risk Management Committee (EIRMC) which is represented by all senior Risk Owners and Risk Managers. EIRMC is responsible for monitoring regular Operational Risk Indicators in accordance with the established policies and procedures and taking corrective actions where deemed necessary.
Types of Operational Risk Exposures and Key Operational Risk Indicators (KORIs)
Operational Risk is inevitable in all the products and processes of the Bank. Operational Risk could emerge in various ways, including fraudulent acts, errors, business disruptions, inappropriate behaviours of employees or external factors. These events could result in financial losses and other damages to the Bank including possible reputational risks.\

Objectives of the Operational Risk Management function of the Bank is to:
- Minimise the impact of losses incurred in the normal course of business (Expected Losses) and to avoid or reduce the likelihood of incurring large extreme (Unexpected) losses.
- To regularly review and improve the business processes and enhance the shareholder value.
Operational Risk unit in the IRMD compiles all operational loss data and other information through various sources and prepare Key Operational Risk Indicators which are reviewed at EIRMC on a monthly basis and submitted to the BIRMC along with the mitigatory measures adopted in reducing such risks. Key Operational Risk Indicators are being improved continuously, where appropriate, to act as early warnings of increased risk of potential losses. Effective tracking of these indicators by the Operational Risk Management function allows the Bank to identify changing risks upon their occurrence and respond to them promptly in the best possible manner. Key Operational Risk Indicators are discussed further, under ‘Operational Risk Monitoring and Reporting’.


